Reliable results in the laboratory begin with reliable instruments. The micropipette is one of the most widely used instruments in research, diagnostics, and life sciences. It is essential for liquid handling. The integrity of an experiment can be jeopardized by even the smallest variations in volume. For reproducibility, compliance, and confidence in every workflow, it is crucial to measure and ensure the accuracy and precision of your micropipette.
This article describes best practices for preserving consistent results in the laboratory, it also explains the distinction between accuracy and precision, and offers a step by step guide to assessing micropipette performance.
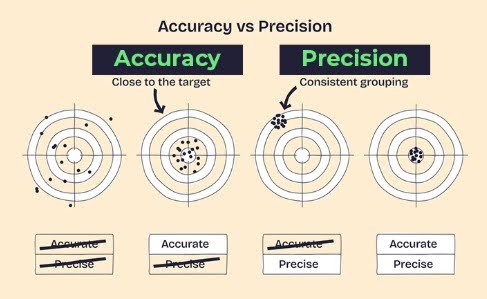
Accuracy vs. Precision in Micropipette
Although the terms are frequently used interchangeably, precision and accuracy refer to two different performance aspects:
- Accuracy refers to how closely the dispensed volume matches the calculated or expected volume. For example, the measurement is inaccurate for instance, if the micropipette is set to 100 µL but yields 98 µL.
- Precision refers to the reproducibility of results when the same volume is dispensed repeatedly. A precise micropipette will deliver nearly identical volumes each time, even if they deviate slightly from the target.
In practice :
- When a micropipette consistently dispenses 95µL rather than 100µL, it can be known as precision but not accuracy.
- Or accurate but not precise (averaging close to 100µL but with high variations between attempts)
Reliability of results is ensured by the micropipette’s accuracy and precision.
Tools Required to Verify Micropipette Performance
Simple lab equipment can be used to test the accuracy and precision of a micropipette. The most popular and advised method is the gravimetric, which is based on weighing water.
You will need:
- A micropipette with compatible tips and a suitable volume range.
- Distilled water at room temperature(20-25°C).
- An analytical balance that can be read at 0.0001 or higher.
- A weighing vessel, such as beaker or small container
- A calculator or data evaluation software tool.
Measuring Accuracy of a Micropipette
Accuracy testing involves comparing the actual dispensed volume with the set volume.
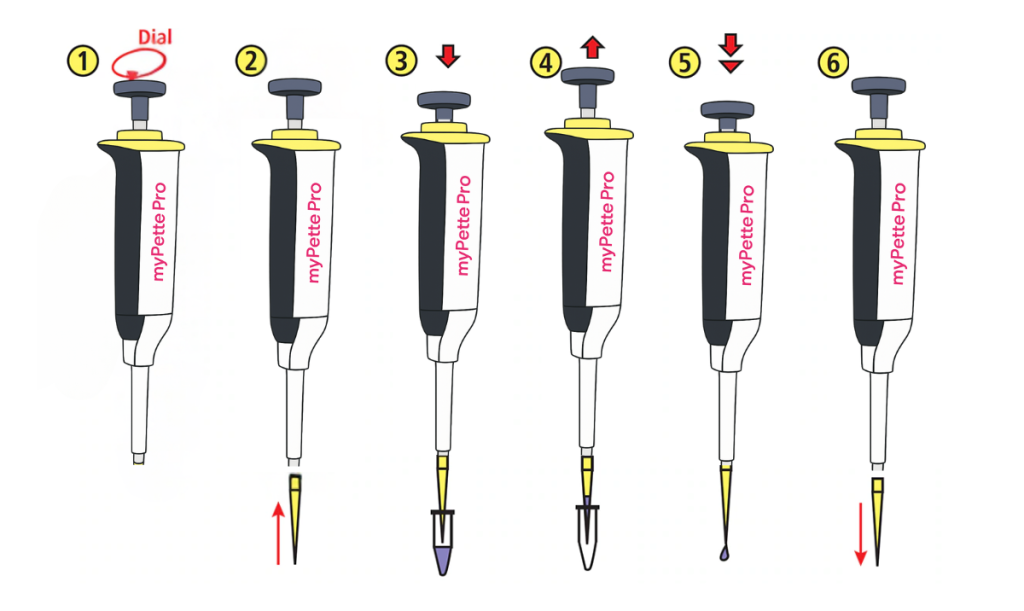
Procedure:
- A specified test volume, such as 100 µL, should be set for the micropipette.
- Aspirate and dispense water once to pre-wet a fresh tip.
- Pour distilled water into the balance’s pre-weighed vessel after aspirating it.
- Note the weight (1 g of water ≈ 1000 µL).
- Repeat the process at least ten times.
- Determine the measured volumes’ mean.
- Use the following formula to compare with the set volume:
Accuracy (%) = [(Mean Measured Volume – Set Volume) ÷ Set Volume] × 100
Example:
This indicates a systematic under-delivery of 2%.
Measuring Precision of a Micropipette
Precision testing evaluates the reproducibility of results across multiple dispenses.
Procedure:
- Repeatedly dispense the same target volume (for example, 100 µL) in the same circumstances.
- Note every value that was acquired from the balance.
- Determine the standard deviation (SD).
- Calculate the coefficient of variation (CV) by applying:
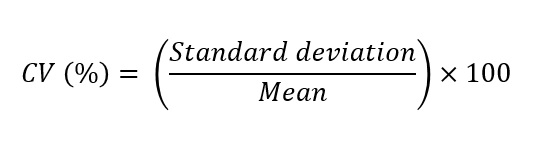
For instance:
98 µL is the mean measured volume.
1 µL is the standard deviation.
CV = (1 ÷ 98) × 100 ≈ 1.02%
Greater precision is correlated with a lower CV. Depending on the volume range, high-quality micropipettes should have a CV significantly below 2%.
Best Practices to Maintain Accuracy and Precision
Ensuring micropipette performance goes beyond initial calibration. Proper handling, technique, and maintenance all contribute to long-term reliability.
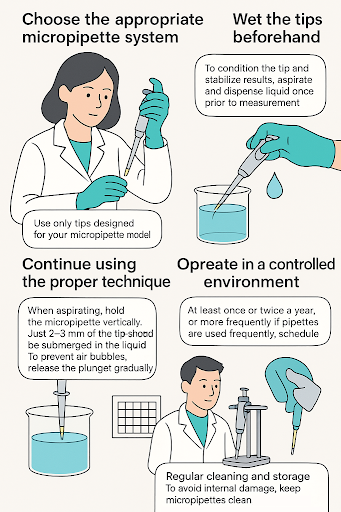
1. Choose the appropriate micropipette system
Use only tips designed for your micropipette model. Inaccuracies, variability, or leakage may result from improperly fitted tips or tips that do not make a proper pipetting system.
2. Wet the tips beforehand.
To condition the tip and stabilize results, aspirate and dispense liquid once prior to measurement.
3. Continue using the proper technique.
- When aspirating, hold the micropipette vertically.
- Just 2–3 mm of the tip should be submerged in the liquid.
- To prevent air bubbles, release the plunger gradually.
4. Operate in a controlled environment
Because water density changes with temperature, perform tests at a steady room temperature.
5. Frequent servicing and calibration
At least once or twice a year, or more frequently if pipettes are used frequently, schedule a professional calibration.
6. Regular cleaning and storage
To avoid internal damage, keep micropipettes clean, adhere to decontamination instructions, and store them upright on stands.
Why Measuring Accuracy and Precision Matters
Reproducibility is a must in diagnostics and research. Just a few microliters of deviation can result in:
- incorrect concentrations of the reagents.
- inconsistent outcomes from one experiment to another.
- Assay failures and resource waste.
Labs can guarantee adherence to quality standards, protect results, and uphold confidence in data integrity by confirming accuracy and precision.
Conclusion
Every laboratory needs micropipettes, and the caliber of research results is directly impacted by how well they work. While precision guarantees consistency, accuracy guarantees correctness. To ensure accurate data, both need to be measured and maintained.
Labs can be sure of their pipetting accuracy by using gravimetric testing, routine calibration, and adherence to best practices. The precision, durability, and ergonomics of AHN Biotechnologie’s micropipettes enable researchers everywhere to consistently produce repeatable results.